The liver which is the largest of the internal organs, plays a major role by producing the proteins required for the body, clotting of the blood, storing the nutrients and sending nutrients to the bloodstream, producing bile which is required for digesting food, storing the sugar, and eliminating harmful substances from the blood. In this process, the liver comes in contact with various harmful substances which scar the liver.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is the final stage of any type of liver damage and happens over a long period of time. The liver tissue is damaged and becomes scarred. The scar tissue cannot perform its functions thereby restricting the flow of blood and reduce the production of proteins, glucose and cholesterol.
Mostly, Cirrhosis is the result of Hepatitis C, alcohol and fatty liver. Once Cirrhosis occurs, it cannot be reversed and more and more tissues get scarred eventually leading to liver failure. Other complications are kidney failure, liver cancer, insulin resistance, diabetes, gallstones, esophageal varices (the bile which cannot pass through the liver is backed up to the esophagus), edema and enlarged spleen.
Though it is fatal, further damage to the liver tissues can be avoided if detected early.
Cause of Cirrhosis
The liver can repair its damaged tissues but with long term exposure of harmful substances like Hepatitis virus and alcohol, Cirrhosis happens. It shrinks and hardens the liver tissue restricting the normal liver function.
Cirrhosis Due to Alcohol
Cirrhosis by alcohol happens when a woman takes more than 2 drinks a day and when a man takes more than three per day for more than 10 years. It however is different for each and every individual.
Cirrhosis Due to Fatty Liver
Cirrhosis due to fatty liver is due to the buildup of fat in the liver. The fat buildup can be in people who may be obese, diabetes, high BP, repeated heart problems and metabolic syndrome which is associated with the size of the person.
Cirrhosis Due to Genes
Cirrhosis can also be genetic, where the person is affected with any of the diseases such as the Wilson’s disease, galactosemia, hemochromatosis, Alpha- 1 antitrysin deficiency and other glycogen storage issues.
Symptoms of Cirrhosis
The symptoms of Cirrhosis are jaundice, loss of appetite, weight loss, weakness, itchiness, nose bleeding, mental confusion, swelling of the abdomen, swelling of the legs, impotence and gynecomastia where breast development occurs in men.
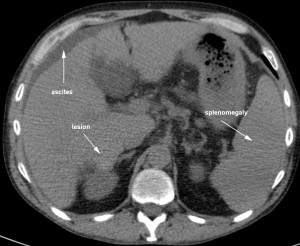
The doctor looks for signs and symptoms and orders for appropriate tests. The tests which can detect Cirrhosis are family history, blood count test, albumin test (shows the rate at which the blood clots), liver function tests, liver biopsy, MRI of the abdomen area, Scan of the liver, CT of the abdomen and alpha fetoprotein which detects the presence of liver cancer.
Cirrhosis when detected can be treated based on its progress. Treatments are based on the extent of liver damage. Surgery is suggested to eliminate the damaged liver tissue and saving the rest of healthy tissues. Liver transplantation is done when there is liver failure due to Cirrhosis. Doctors prescribe a low protein and high carbohydrate diet. Reduced salt intake and stopping alcohol consumption is advised. Cirrhosis can be prevented or slowed by following a healthy lifestyle and stopping alcohol consumption.
Liked this article on Cirrhosis Of The Liver and have something to say? Comment below and don’t forget to SHARE THIS ARTICLE!